40 under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to secondary deviance?
Secondary Deviance: Definition & Examples - Study.com Primary deviance is a deviant act that receives little social reaction or mild, corrective reaction. It's important to remember that not all deviant acts produce long-term negative outcomes. Some... Neutralization Theory - Criminology - Oxford Bibliographies Sykes and Matza outlined five neutralization techniques: denial of responsibility, denial of injury, denial of victims, appeal to higher loyalties, and condemnation of condemners. Research on the theory has generally produced mixed results, leading many to conclude that the theory is not powerful enough to serve as a stand-alone explanation for ...
Sociology Exam 2 Flashcards - Quizlet Under what circumstances does a deviant label transition from primary to secondary deviance? a.when the deviant label is internalized b.when the deviant label is applied by a large number of people c.when the deviant label is applied later in life d.when the deviant label is applied by someone very powerful a.when the deviant label is internalized
Under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to secondary deviance?
Because of ________, deviance is often seen as mental sickness rather ... Secondary deviance describes a situation in which a person has been publicly identified as deviant, such as by being classified as mentally unstable or criminal. Labeling theory emphasizes that being labeled can generate a self-fulfilling prophecy whereby others behave toward the labeled person in ways that confirm or reinforce the label. Underwhatcircumstancesdoesadeviantlabelleadfromprimarytosecondarydevian ... Under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to secondary deviance? a. when the deviant label is applied by a large number of people b. when the deviant label is applied by someone very powerful c. when the deviant label is internalized d. when the deviant label is applied later in life e. when the deviant label concerns a ... Deviance | Boundless Sociology | | Course Hero Stigma plays a primary role in sociological theory. Émile Durkheim, one of the founders of the social sciences, began to address the social marking of deviance in the late nineteenth century. Erving Goffman, an American sociologist, is responsible for bringing the term and theory of stigma into the main social theoretical fold.
Under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to secondary deviance?. Deviant Social Behaviors that have become Acceptable In keeping with the strictures against premarital sex, it was deviant behavior for a single man and single woman to spend the night together. The 1960's and 70's saw more and more young couples move in together without getting married (although many did marry later on). By the 80's, many middle aged and older couples were doing the same. The Conflict Perspective on Deviance - Course Hero Deviance, in a sociological context, describes actions or behaviors that violate social norms, including formally-enacted rules, as well as informal violations of social norms. In sociology, conflict theories are perspectives that emphasize the social, political, or material inequality of a social group, that critique the broad socio-political ... Deviance Theories | Encyclopedia.com Since its inception as a discipline, sociology has studied the causes of deviant behavior, examining why some persons conform to social rules and expectations and why others do not. Typically, sociological theories of deviance reason that aspects of individuals' social relationships and the social areas in which they live and work assist in ... Deviance (sociology) - Wikipedia Jump search Action behavior that violates social norms.mw parser output .hatnote font style italic .mw parser output div.hatnote padding left 1.6em margin bottom 0.5em .mw parser output .hatnote font style normal .mw parser output .hatnote link...
Sociology 200 Chapter 6 Flashcards - Quizlet Under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to secondary deviance? when the deviant label is accepted as part of one's identity Deviance occurs in all cultures and is impossible to completely get rid of in society. True Under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to ... The circumstance that can lead a deviant label from primary to secondary deviance is when the deviant label is applied later in life What is labelling theory? According to the labeling hypothesis, the terminology used to define or categorize people may determine or have an impact on their behavior and sense of self. Sociology: Exam #2 Flashcards - Quizlet Under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to secondary deviance? when there are social or legal sanctions and the deviant label is internalized _____ work is the dominant form of employment in the postindustrial economy. Service Sociology Unit 2 Flashcards - Quizlet How secondary groups lead to primary groups. ... How can deviance be explained by the functionalist perspective. through strain theory. ... Under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to secondary deviance? when the deviant label is accepted by the individual and seen as deviant.
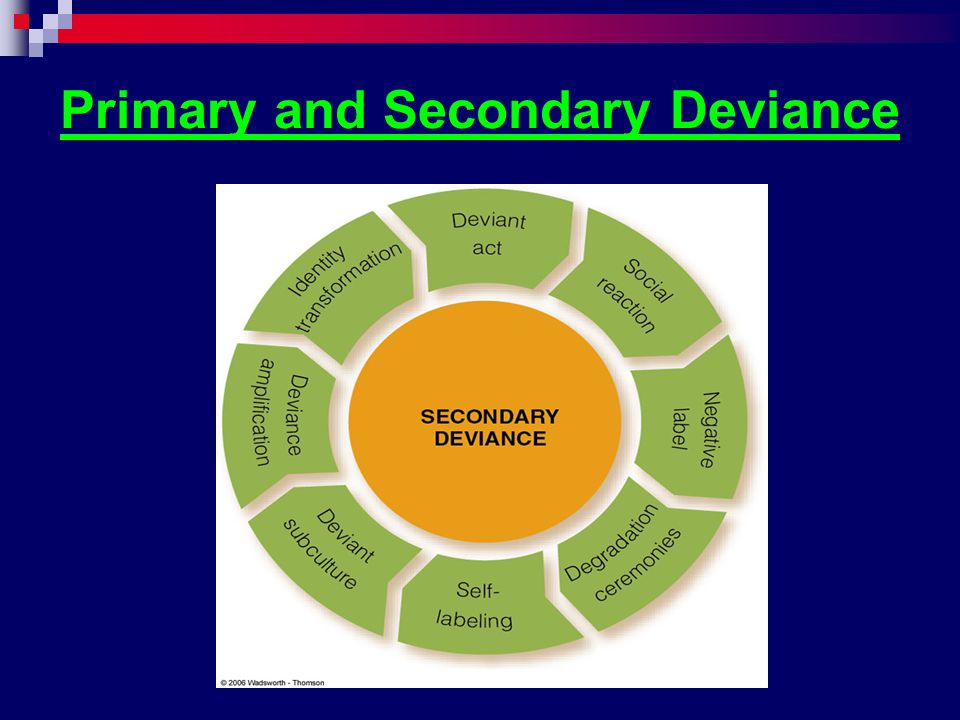
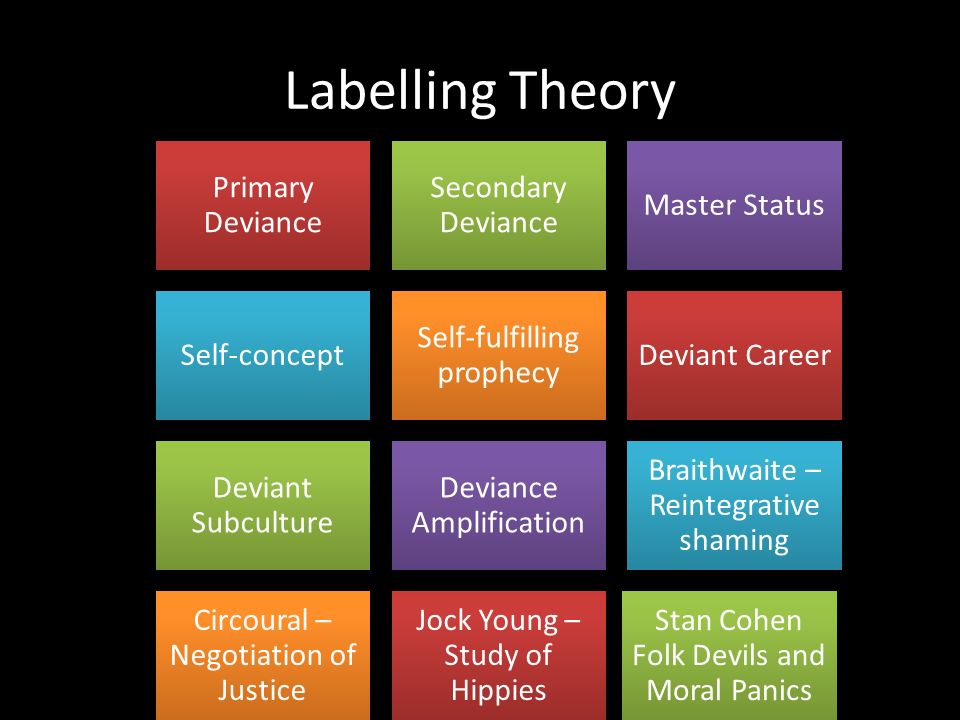
Labeling Theory of Deviance: Definition & Examples Secondary deviance, on the other hand, refers to acts that are labeled by the society as deviant and attached to one's identity thus affecting one's self-concept. What is labeled as deviant depends on the legal forces of the society and the law that the society entails, thus what is labeled as deviant will differ from society to society? About What is Sociology _Autosaved - DocShare.tips Labeling theory calls attention to two kinds of deviance. A. B. Primary Deviance Secondary Deviance This refers to the act of breaking a rule. Henslin (2004:146) notes that sometimes people become more deviant as a result of being labeled as deviant. This happens because the label becomes a part of the person's self-concept. Under what circumstances, the Puma Swaraj was demanded by the Congress ... under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to secondary deviance? by Get Answers Chief of LearnyVerse (321k points) asked in Other Sep 10, 2021. 0 votes. 83 views 1 answer. under which of the following circumstances would we observe the greatest increase in real income? Part III - Putting Case Studies to Work: Applications to Development ... The Case for Case Studies - May 2022
Theories of Crime and Deviance | Boundless Sociology - Course Hero Labeling theory refers to the idea that individuals become deviant when a deviant label is applied to them; they adopt the label by exhibiting the behaviors, actions, and attitudes associated with the label. Labeling theory argues that people become deviant as a result of others forcing that identity upon them.
under what circumstances will a judge grant a motion for a new trial? Mention three circumstances in which the office of the Judge of the Supreme Court falls vacant. ... In the following sentence elaborate the parts given in bold. Under the circumstances it was a very unfortunate remark for the bird to make. by tony# ... under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to secondary deviance? by Get ...
Labelling Theory of Crime - A Summary - ReviseSociology Cicourel - first stage - working class kids more likely to be labelled as deviant by police; second stage - more likely to be prosecuted by courts, most of this is based on appearance and language, not the deviant act. Labelling has real consequences - it can lead to deviancy amplification, the self-fulfilling prophecy and deviant careers
Chapter 7. Deviance, Crime, and Social Control - Introduction to ... Deviance and Control. Deviance is a violation of norms. Whether or not something is deviant depends on contextual definitions, the situation, and people's response to the behaviour. Society seeks to limit deviance through the use of sanctions that help maintain a system of social control.
Under what circumstances does a deviant label lead - Course Hero 49. Under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to secondary deviance? a. when the deviant label is applied by a large number of peopleb. when the deviant label is applied by someone very powerful c. when the deviant label is accepted by the individuald. when the deviant label is applied later in life ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Easy ...
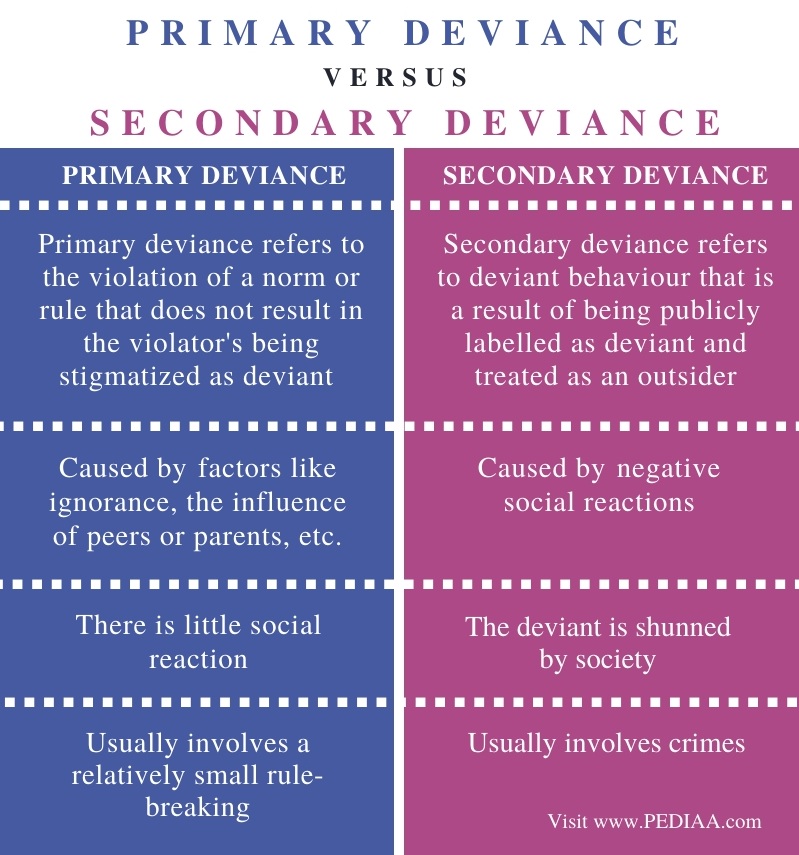
Are the functions of deviance? - duties.pakasak.com Explain the two types of deviance associated with labeling theory. Primary deviance: this is nonconformity that goes undetected by those in authority. Secondary deviance: this results in the individual being labeled as deviant and accepting the label as true. The explanation of deviance as a learned behavior.
18. Under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to ... answered 18. Under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to secondary deviance? a. when the deviant label is applied by a large number of people b. when the deviant label is applied by someone very powerful c. when the deviant label is internalized d. when the deviant label is applied later in life
Difference Between Primary and Secondary Deviance In primary deviance, the person commits a deviant action without knowing that h/she is going against the norm system. However, in secondary deviance, the person is already labeled as a deviant but still h/she continues to engage in that particular act. Now, we will look at these two terms, primary deviance and secondary deviance, in detail.
under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to ... Under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to secondary deviance? a. when the deviant label is applies by a large number of people to that individual b. when the deviant label is applied by someone very powerful c. when the deviant label is accepted by the individual and seen as deviant
Sociology Quiz #3 Flashcards | Quizlet a. the absolute distinction between primary and secondary groups b. the goal-orientated nature of primary groups c. the way that primary groups can lead to membership in secondary groups d. the way that secondary groups can lead to close personal ties of primary groups e. the relative distinction between primary and secondary groups
Deviance | Boundless Sociology | | Course Hero Stigma plays a primary role in sociological theory. Émile Durkheim, one of the founders of the social sciences, began to address the social marking of deviance in the late nineteenth century. Erving Goffman, an American sociologist, is responsible for bringing the term and theory of stigma into the main social theoretical fold.
Underwhatcircumstancesdoesadeviantlabelleadfromprimarytosecondarydevian ... Under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to secondary deviance? a. when the deviant label is applied by a large number of people b. when the deviant label is applied by someone very powerful c. when the deviant label is internalized d. when the deviant label is applied later in life e. when the deviant label concerns a ...
Because of ________, deviance is often seen as mental sickness rather ... Secondary deviance describes a situation in which a person has been publicly identified as deviant, such as by being classified as mentally unstable or criminal. Labeling theory emphasizes that being labeled can generate a self-fulfilling prophecy whereby others behave toward the labeled person in ways that confirm or reinforce the label.































Post a Comment for "40 under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to secondary deviance?"